Problem Tree
Diagram that maps problems and places critical issues according to cause-and-effect relationships facilitating discussion and identification of critical issues on which to intervene strategically.
Download The manual for the use of the instrument with suggestions e instructions.
For an in-depth theoretical study click here.
Your opinion is important to us. Please rate the tool based on your experiences or for how you would like to use it.
Take advantage of the new free service "Remote Lab". Request an appointment by filling out the form.
Tips
Indications from the DRLab experience for using the tool.



Instructions for compilation
Foreword. Start from problems known to the working group.
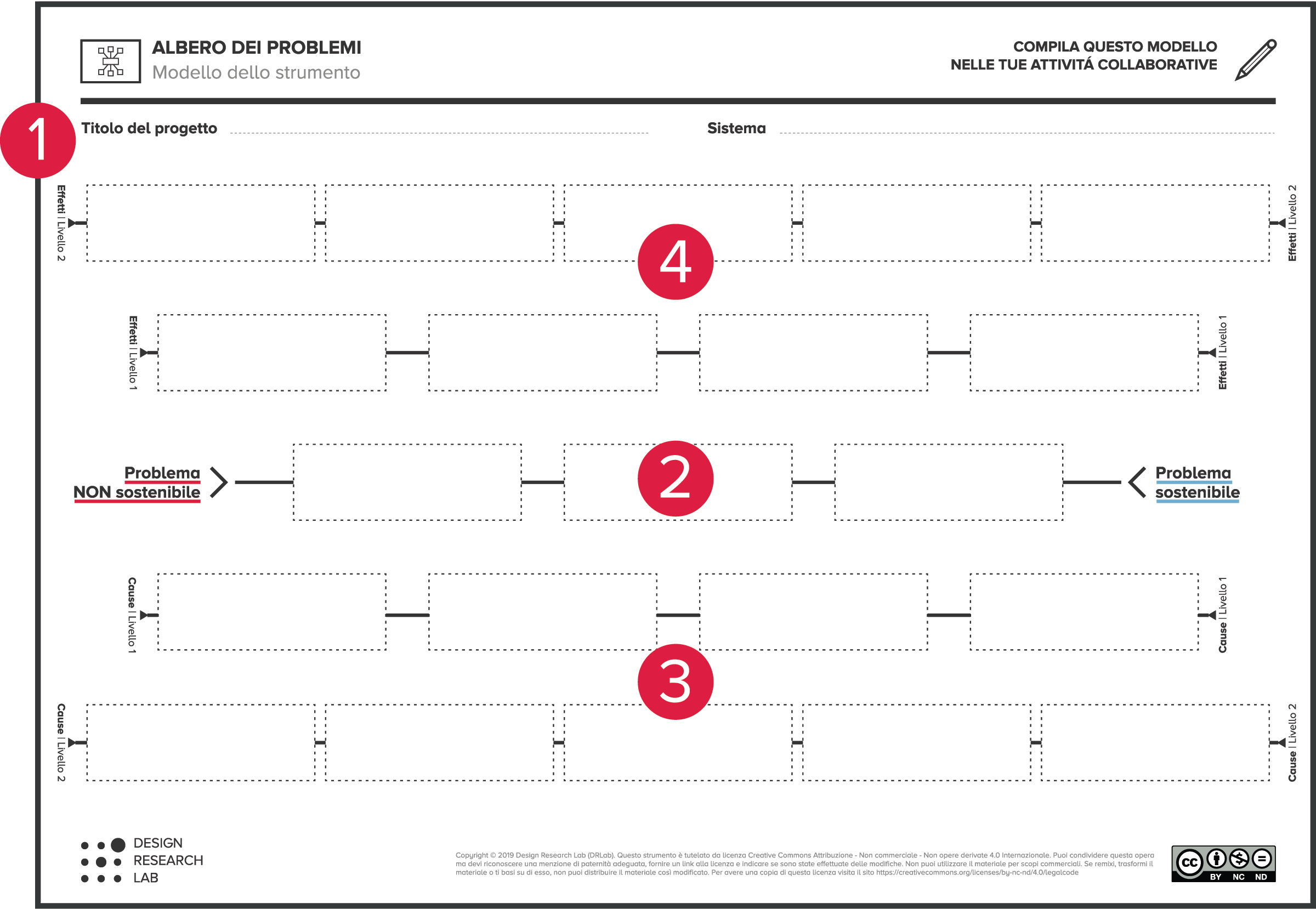
1. Indicate the title of the project. Indicate the reference system being analyzed by the tool.
2. List the main problems identified in the reference system and note a definition of them along the middle row. Indicate on the left the least sustainable problems, those that are seemingly insurmountable or externally dependent, and on the right the problems perceived to be more sustainable instead.
3. Starting from the middle row, indicate downward, the causes of the main problems already identified, arranging them on two levels according to the cause-effect dynamics. Attention, at this stage it is useful to use post-its to be able to move the identified problems by readjusting the cause-effect dynamics in accordance with the evolution of the reflections.
4. Starting from the middle row, indicate upward the effects and consequences of the main problems already identified, organizing them on two levels according to the cause-and-effect dynamics. Again, the use of post-it notes to readjust the dynamics is recommended.
N.B. The use of post-it notes facilitates the evolution of mapping by making it easily practicable and modifiable to understand problems with respect to both their correct affiliation with causes rather than effects and their degree of sustainability with respect to their possible solution.
N.B. When the effects of an as-yet undefined problem are known, it may be useful to use the tool starting with the effect rows and gradually moving downward-always according to cause-effect logic-attempting to identify the causes of those effects. Only later will this operation allow more precise identification of the problem highlighted in the middle row by understanding how sustainable it actually is.
Share your experience with us and strengthen your skills.
Please contact us if you would like to share your experience of using the tool, or if you have doubts and want to use it but do not know how.